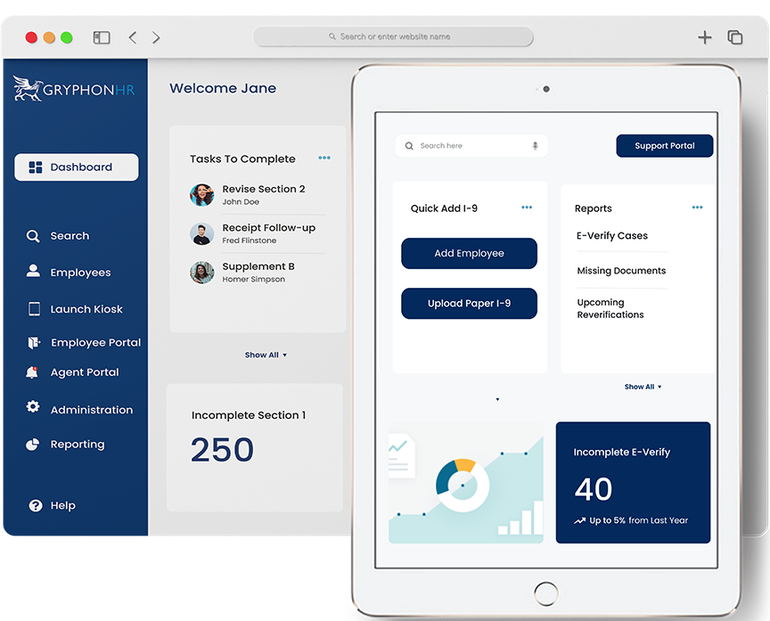
Discover a Better I-9 Compliance Solution
Improve compliance with Form I-9 and E-Verify® and provide a better electronic I-9 and onboarding experience to your team and employees with an intuitive cloud platform. Learn more about our remote I-9 verification options and virtual I-9 verification features.
Crafted for Significant Advantages
Streamlined I-9 Compliance
Stay on top of current Form I-9 compliance requirements with technology that adapts and evolves.
Easy for Everyone
Allows anyone to complete the Form I-9 easily, while increasing compliance and efficiency.
Resolves Logistical Challenges
Resolve logistical challenges of meeting Section 2 requirements and enjoy greater flexibility for I-9 verification.
Virtual Verifications + E-Verify
Helps E-Verify employers to efficiently and accurately complete Form I-9 and better manage E-Verify cases.
Consistent I-9 Procedures
Creates consistent company procedures to help avoid non-compliance and discriminatory practices.
Customizable & Configurable
Customizable and configurable to meet your HR and business needs, no matter the scale or structure.
Compliant
Our cloud platform is always meets current I-9 requirements and helps to ensure I-9s are always completed correctly, and on-time.
Customizable
Configure our I-9 solution to meet the specific needs of your business, including: branding, user roles, permission sets, and more.
Easy-to-use
Simplify complex compliance requirements and create a better onboarding experience with our intuitive and easy-to-use cloud software.
Secure
Ensure safe and compliant retention and storage of your I-9s and data. Your data is always protected with the highest level of security standards.
GryphonHR has been a game-changer! Our team has reduced the time it takes to process I-9's and we couldn't be happier with the platform!
- VP of HR, Rising Phoenix Creative
Form I-9 and Technology Experience
Our Form I-9 and E-Verify compliance experts stay on top of ever-changing employment eligibility requirements to help ensure compliance. Streamline and simplify the employment process with an intuitive Form I-9 platform that evolves to meet the latest tech standards.
I-9 Accuracy & Efficiency
Reduce the time spent processing I-9 forms and ensure accurate completion with intuitive workflows, data validation, and guidance. GryphonHR ensures every field of the Form I-9 is completed properly, within the correct time frames. Tracking, notifications, and alerts help you to stay on top of your Form I-9 and E-Verify progress.
Complete Form I-9 for both onsite and remote employees through a single platform without worrying about additional modules or fees. Our flexible I-9 verifier options make it easy to choose the right authorized representative based on the needs of your business and budget. You can even build your own internal reusable I-9 verification network.
Seamless Integrations
Integrate with your existing HR or payroll system through our REST API and easily access the I-9 cloud platform with single sign-on. You can also choose to access the system as a stand alone solution. Our electronic I-9 integration options adapt to the specific needs of your organization.
Discover Our Form I-9 Software Capabilities

Advanced E-Verify Integration
Our E-Verify integration and workflows enable you to automate the submission of Form I-9 to the E-Verify system and easily manage cases. You can expedite E-Verify workflows with quick and accurate photo matching and and resolve issues and TNC’s with greater efficiency. Reporting features include an E-Verify cases summary to help you stay on track. Get in touch with an I-9 expert today to learn more about our robust E-Verify features.
Become a Partner
Learn more about becoming a partner and offer your clients a leading-edge Form I-9 and E-Verify platform.

Form I-9 News & Updates